Diagnosis and correcting an old problem with new tools: Industrial Internet of Things Pump Monitoring
Diagnosis and correcting an old problem with new tools: Industrial Internet of Things Pump Monitoring
The Problem: For decades pump rental companies have wondered how customers have been utilizing pumps in the field. A pump rental company began using Cornell Co-Pilot to monitor pumps to answer that question in late 2019.
The company had only rudimentary operational intelligence on their rental pumps; beyond run time on the engine, usage was self-reported by the end user. Equipment could break down during operation, proving detrimental to productivity for both the end user and the rental outfit. It is often the case that if the pump goes down, the whole job can shut down for repairs—costing thousands of dollars in opportunity cost to the end user and repairs to the rental company.
The Solution: This is where Co-Pilot fits in. By installing Co-Pilot on their fleet of pumps, this rental company is able to track where their equipment is, how it is being utilized, how often it is used, and the total hours of usage, all remotely from the desktop or mobile applications.
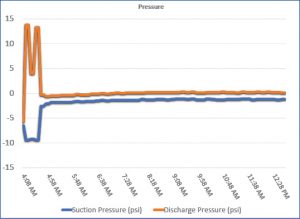
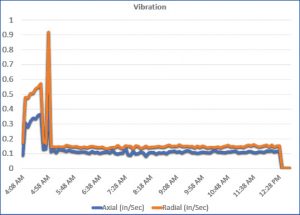
The Co-Pilot provided immediate results when it captured a pump that was running dry for hours at a time. It was clear in the data that for the first hour of operation, the pump was running at a higher vibration, and suction/discharge pressures were normal. For the remaining 6 plus hours, vibration dropped to a much lower level, and pressures dropped off to zero. This type of operation causes wear and tear on the pump, adds unnecessary hours to the engine, and consumes excessive fuel. The rental company was able to contact the pump user on site, discuss the scenario and provide valuable insight in correcting the issue. This added level of customer service goes a long way and is a win-win for both parties, saving time and money in unnecessary down time and repairs.
Devices for Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) monitoring, such as Cornell Co-Pilot, have many advantages to equipment owners and end-users above and beyond seeing how your pump is running right now. They include:
- Better asset management: Through GPS location tracking, know exactly where a piece of equipment is at all times. Track how often it is moved, when it has been used, under what conditions, and do so quickly.
- Predictive maintenance: As the system learns running conditions and operations, Co-pilot users can better predict when parts will wear, and order and replace prior to a costly unplanned shutdown. Alerts can be set up and sent to immediately notify of out of spec conditions.
- Plan Maintenance: Real-time information regarding operating hours, bearing frame temperatures, fuel levels etc. allow maintenance teams to better react and efficiently plan for upcoming equipment service needs. Using GPS location tracking, equipment can be found quickly and serviced as required.
- Better onsite access and understanding: Allows users in front of equipment to easily access dimensional prints, pump curves, operation manuals, and order replacement parts.
- Predictive forecasting: As pump users gather data on their average life cycle for machinery, they can make better forecasts than traditional historical models.
- Greater energy efficiency: Operating the rotating equipment at better points on the pump curve can be possible with operational data. A few percentage points of efficiency gained on a piece of equipment running several thousand hours a year can be thousands of dollars in savings.
- Improved operational efficiency: Smarter, more timely decisions can come from data, offering improved overall efficiency.
- Greater safety: With rotating equipment sending signals—even shutting down—if it is outside of established parameters, the equipment can be run more safely for everyone on-site.
- Business analytics: Data from connected pumps can be analyzed, overlaid, and shared. Mission critical insights can be shared with on-site and off-site teams. Better uses and cases can be explored.
- Reduce warranty claims: By knowing how your equipment is operated, actions can be taken before damage occurs. This reduces downtime to the end-user and protects equipment for the owner, while providing a higher level of customer service.
 Cornell Co-Pilot™ is a pump monitoring and analytics system designed for use to improve pump operation and performance. A typical Co-Pilot system includes the Co-Pilot module connected to the Co-Pilot cloud-based monitoring platform. Learn more about Cornell Co-Pilot at co-pilot.cornellpump.com
Cornell Co-Pilot™ is a pump monitoring and analytics system designed for use to improve pump operation and performance. A typical Co-Pilot system includes the Co-Pilot module connected to the Co-Pilot cloud-based monitoring platform. Learn more about Cornell Co-Pilot at co-pilot.cornellpump.com
Related Literature
[pods name=”library” slug=”88″ template=”Library Item Display”]